Madagascar has a diverse but mainly endemic frog fauna, the biogeographic history of which has generated intense debate, fueled by recent molecular phylogenetic analyses and the near absence of a fossil record. Here, we describe a recently discovered Late Cretaceous anuran that differs strikingly in size and morphology from extant Malagasy taxa and is unrelated either to them or to the predicted occupants of the Madagascar–Seychelles–India landmass when it separated from Africa 160 million years ago (Mya). Instead, the previously undescribed anuran is attributed to the Ceratophryinae, a clade previously considered endemic to South America. The discovery offers a rare glimpse of the anuran assemblage that occupied Madagascar before the Tertiary radiation of mantellids and microhylids that now dominate the anuran fauna. In addition, the presence of a ceratophryine provides support for a controversial paleobiogeographical model that posits physical and biotic links among Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent, and South America that persisted well into the Late Cretaceous. It also suggests that the initial radiation of hyloid anurans began earlier than proposed by some recent estimates.
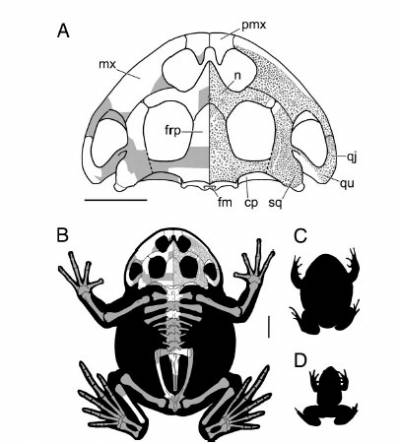
Beelzebufo ampinga, Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. (A) Skull reconstruction showing parts preserved (white areas, Left) and distribution of pit-and-ridge ornament (stippling, Right). (B) Skeletal reconstruction and inferred body outline of average-sized (skull width, 200 mm; SVL, 425 mm) adult female B. ampinga based mainly on Lepidobatrachus asper (32). White areas indicate parts represented by fossil specimens. For size comparison, dorsal view silhouettes of Ceratophrys aurita (the largest extant ceratophryine) (C), and Mantidactylus guttulatus (the largest extant Malagasy frog) (D), are shown. cp, crista parotica; fm, foramen magnum; frp, frontoparietal; mx, maxilla; n, nasal; pmx, premaxilla; qj, quadratojugal; qu, quadrate; sq, squamosal. (Scale bars: 50 mm.)
|